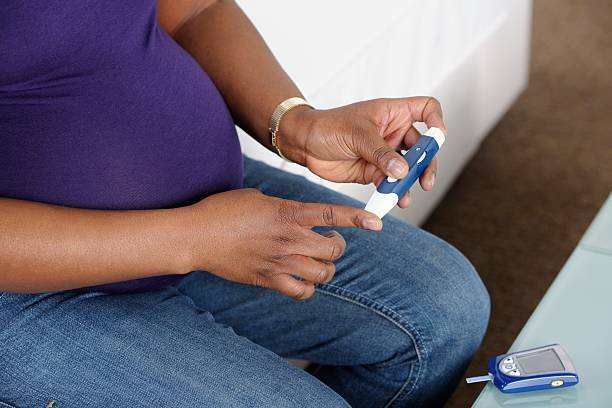
What is tyape 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
It is the most common form of diabetes and typically develops in adults, though it is increasingly being diagnosed in younger individuals due to lifestyle changes.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of factors, including genetic predisposition, being overweight, and physical inactivity.
High-calorie diets and sedentary lifestyles significantly contribute to the development of insulin resistance.
The natural history of the disease - Without effective treatment
Without effective treatment, Type 2 diabetes can lead to uncontrolled high blood sugar, causing damage to the eyes, kidneys, heart, nerves, and blood vessels.
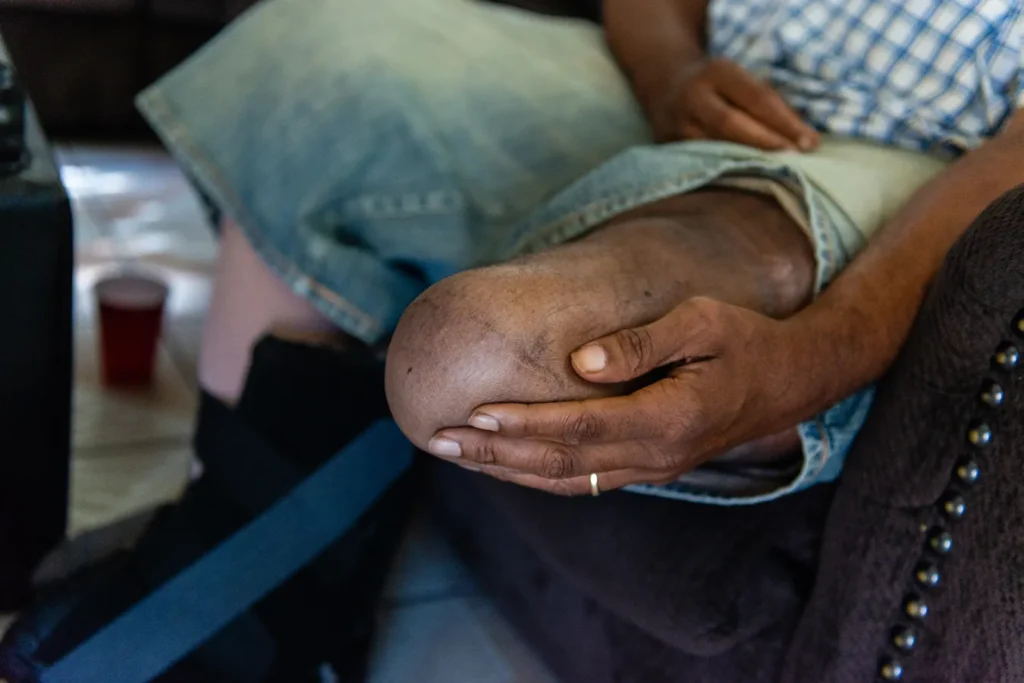
Over time, complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness may develop. Diabetic foot ulcers may also occur, potentially leading to amputations if untreated.
How is Type 2 diabetes managed - Treated
Management involves lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular exercise. Many people with Type 2 diabetes need oral medications or insulin injections to control their blood sugar.
Blood sugar levels must be regularly monitored, and patients need periodic check-ups to adjust treatments and screen for complications.
Key Risk Factors
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to insulin resistance.
- Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 45.
- Family History: Having a parent or sibling with Type 2 diabetes raises the risk.
- Race/Ethnicity: Certain populations, such as African, Hispanic, and Asian communities, are at higher risk.
- Gestational Diabetes: Having diabetes during pregnancy can increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later.
Complications if untreated or poorly treated
The many complications of diabetes
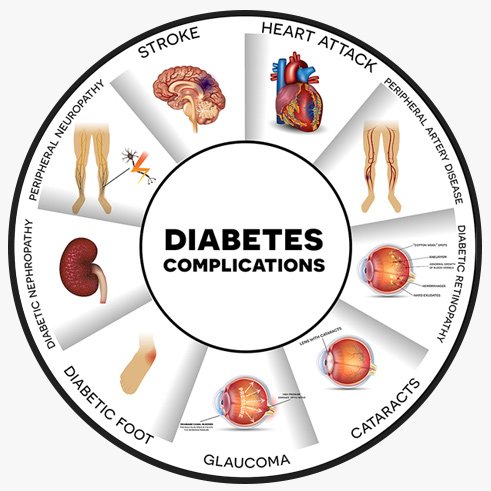
Uncontrolled or poorly treated Type 2 diabetes can lead to:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Kidney Disease: Can lead to kidney failure and the need for dialysis.
- Nerve Damage: Can cause pain, numbness, and poor wound healing, leading to infections or amputations.
- Eye Damage: Diabetic retinopathy can cause blindness.
- Foot Problems: Poor circulation and nerve damage increase the risk of severe infections and amputations.
A diabetic patient with an amputated left leg
The most important actions needed to be taken
By Everyone – To stay away from the disease:
- Maintain a healthy weight and balanced diet.
- Engage in regular physical activity to reduce insulin resistance.
- Be aware of the risk factors and symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Get regular check-ups, especially if you have any of the risk factors for Type 2 diabetes discussed earlier.
By those already affected by the disease:
- Follow prescribed medications and insulin therapy as directed.
- Monitor blood sugar levels consistently.
- Make lifestyle changes such as improving diet and increasing physical activity.
- Attend regular medical appointments for ongoing monitoring and to screen for complications.
Remember
Type 2 diabetes is a manageable condition with the right treatment and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and proactive management are essential to prevent serious complications and improve quality of life.